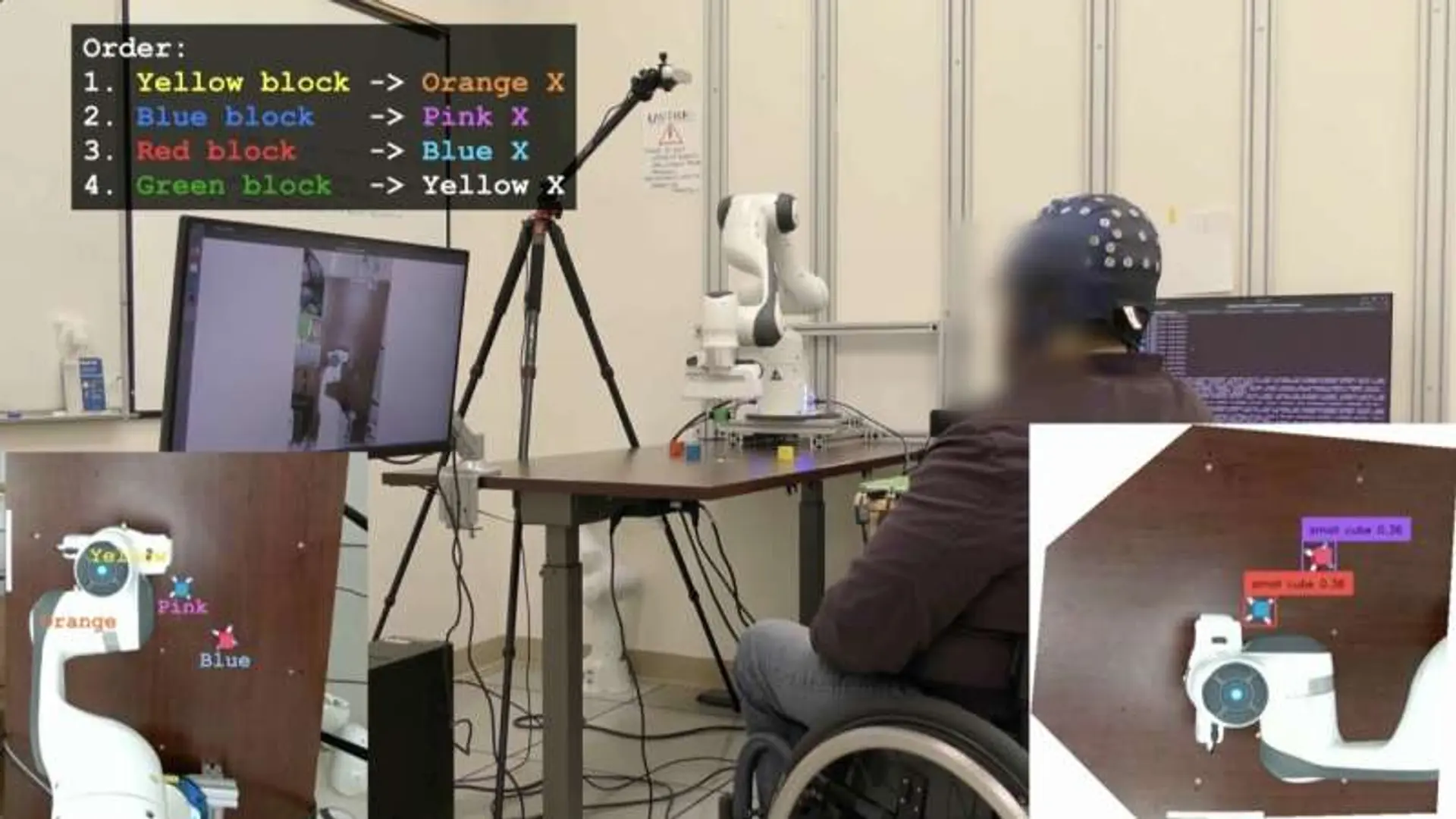
UCLA engineers have created a non-invasive, wearable brain-computer interface (BCI) that uses artificial intelligence to interpret user intentions. The system allows users to control a robotic arm or computer cursor.
The AI functions as a 'co-pilot,' assisting in the completion of tasks by decoding brain signals. This advancement could significantly improve the usability and efficiency of BCI technology for individuals with motor impairments. The wearable nature of the device also promotes greater user comfort and accessibility.
This technology represents a step forward in the development of intuitive and responsive BCIs, potentially leading to enhanced assistive devices and human-machine interaction.
Related Articles
aiartificialintelligenceintelligencebraincomputerinterfaceroboticsuclaassistivetechnology

Optical AI models emerge
Read more about Optical AI models emerge →
Precision Farming Stabilises Food Prices
Read more about Precision Farming Stabilises Food Prices →
Robotics and AI Convergence
Read more about Robotics and AI Convergence →
Robot Olympics Kicks Off
Read more about Robot Olympics Kicks Off →