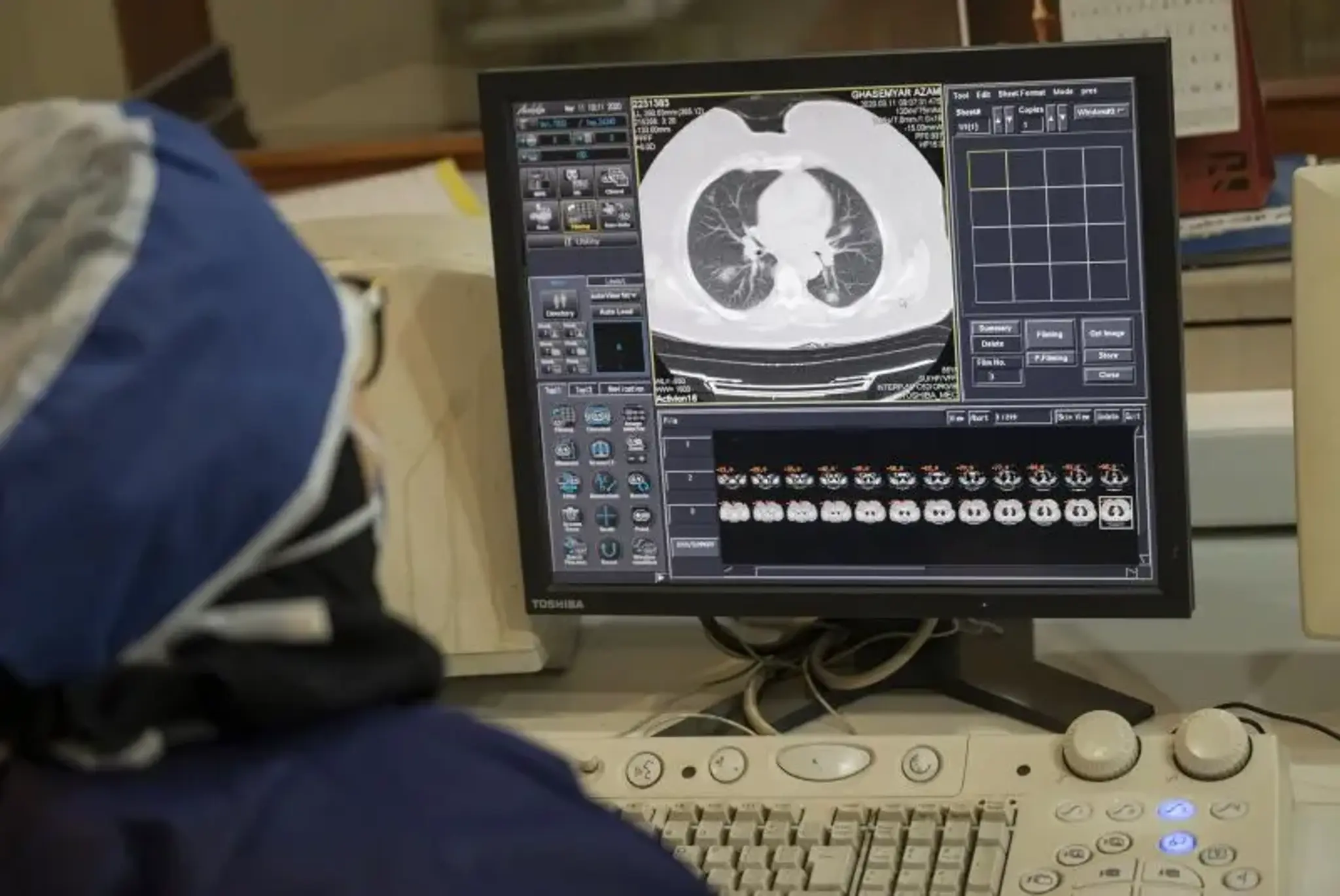
An artificial intelligence (AI) tool called Sybil shows promise in predicting lung cancer risk, particularly among non-smokers. The study highlights an increasing incidence of lung cancer in non-smokers, especially young East Asian women, prompting the need for more accurate risk assessment methods. Sybil analyses CT scans to identify subtle patterns indicative of potential cancer development, even before symptoms appear.
The AI's predictive capabilities could enable earlier detection and intervention, improving patient outcomes. Researchers trained Sybil on a large dataset of CT scans, enabling it to recognise patterns associated with increased lung cancer risk. The tool's accuracy in identifying high-risk individuals could lead to more targeted screening programs and personalised prevention strategies.
This development represents a significant step forward in leveraging AI for proactive healthcare. By identifying at-risk individuals early, Sybil has the potential to reduce the burden of lung cancer and improve survival rates, especially in vulnerable populations.